The surge in popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) in India has brought forth a wave of competition and innovation in the charging infrastructure industry. This raises the crucial question of which type of charger is best suited for your EV. In this article, we aim to provide a straightforward breakdown of the distinctions between AC and DC chargers, bridging the gap between your EV’s charging requirements and a sustainable future.
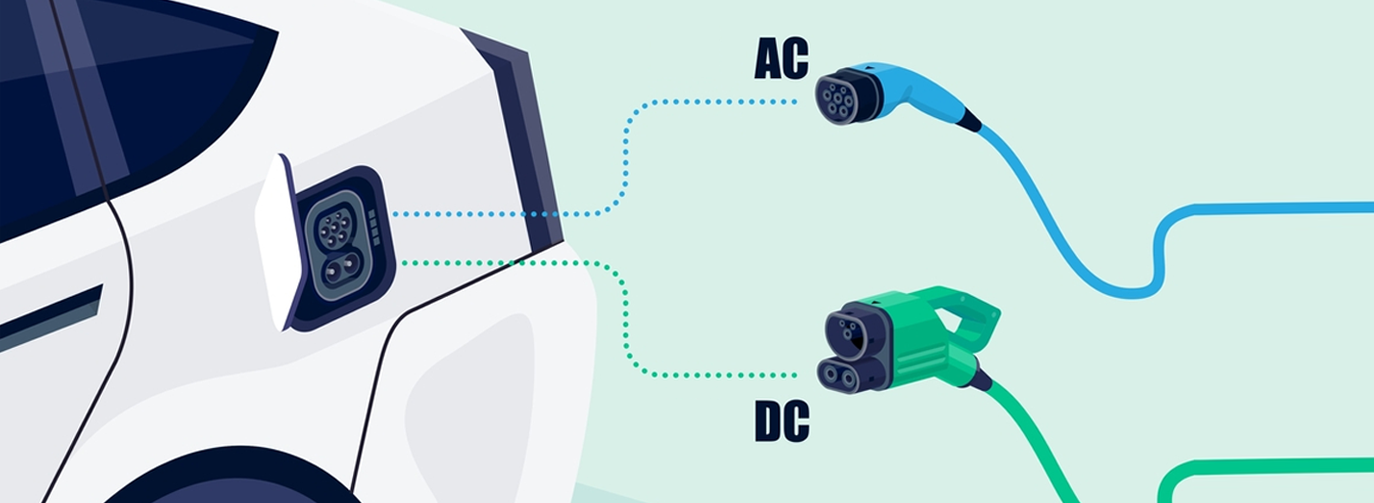
EV chargers come in two primary forms: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). These chargers play a pivotal role in determining the convenience, speed, and efficiency of your EV charging experience.
Technical Differences DC Charger and AC Charger
AC chargers are further classified into Type 1 and Type 2, with Type 1 featuring a 15-amp outlet and Type 2 boasting a 32-amp outlet. On the other hand, DC chargers, often referred to as Level 3 or fast chargers, offer rapid charging and are commonly found in public locations or along highways for quick on-the-go charging.
AC chargers use a rectifier within the EV to convert AC power to DC power for battery recharging. Conversely, DC chargers have the rectifier built into the charger itself, directly providing DC power to the battery. DC chargers can also communicate with the EV’s Battery Management System (BMS), offering real-time information about the battery’s status, such as charge percentage and estimated recharge time.*
Let’s delve deeper into understanding the key differences between these two charging technologies.
Characteristics of AC Chargers

- Charging Speed
AC chargers come in various power ratings, typically ranging from 3 kW to 22 kW. Charging speed depends on the charger’s power rating and your EV’s onboard charger capacity. For instance, a 7 kW AC charger can add approximately 25-30 miles of range per hour to your EV, while a 22 kW charger provides much faster charging, making it suitable for commercial charging stations.
- Compatibility
AC chargers are highly compatible with a wide range of EVs, making them a versatile choice for most EV owners.
- Cost-Efficiency
Installing and maintaining AC chargers is generally more cost-effective than DC chargers, making them appealing for residential and workplace charging solutions.
Characteristics of DC Chargers:

- Charging Speed
DC chargers are substantially faster than AC chargers, offering power levels from 15 kW to 350 kW or more. This allows for quick, substantial range replenishment during short stops, making long-distance EV travel more feasible.
- Compatibility:
Not all EVs support DC fast charging, which may limit its usage. It’s essential to check your EV’s compatibility before relying on DC fast chargers.
- Cost & Infrastructure
DC fast chargers are more expensive to install and maintain than AC chargers. They also require robust electrical connections and cooling systems to manage high charging speeds. Consequently, they are typically found in rest areas, travel routes, and urban hubs where fast, on-the-go charging is vital.
Choosing the Right Charger for Your Electric Vehicle
Your choice between AC and DC charging depends on factors such as your EV model, driving patterns, and charging requirements.
AC Chargers: Ideal for home or workplace charging with overnight charging capability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility for daily commuting and short trips.
DC Chargers: Suited for long road trips, offering rapid top-ups and expanding EV accessibility into remote areas with limited charging infrastructure.
Radius EVCD: Reviving the Present, Empowering a Resilient Future:
DC fast chargers can provide significantly higher power output, which is beneficial for quick battery replenishment. However, this power can generate excess heat, potentially impacting battery health and overall vehicle performance.
In contrast, AC chargers offer a reliable, gentle charging experience without harming the battery. They are also known for their cost-effectiveness.
Considering these advantages and the unique needs of Indian EV owners, Radius Synergies presents an innovative solution: the Electric Vehicle Charging Dock (EVCD). Let’s explore the remarkable benefits of Radius EVCD:
- Power Efficiency: Delivers consistent, safe charging, reducing battery stress.
- Battery Health: Gentle on the battery, extending its lifespan.
- Ease of Installation: Plug-and-play design for effortless setup.
- Voltage Fluctuation Protection: Automatic shutdown during voltage fluctuations.
- On-Spot Billing: Cloud-enabled app for convenient, transparent billing.
- Compatibility: Suitable for various e-mobility vehicles, including e-rickshaws, e-golf carts, e-cars, and e-scooters.
- Versatility: Ideal for residential buildings, commercial spaces, shopping malls, and more.
Radius Synergies’ AC EVCD not only provides a dependable and safe charging solution but also contributes to electric mobility’s sustainability and accessibility.
As the electric vehicle market continues to expand, both AC and DC charging infrastructure will play pivotal roles in making EV ownership accessible and convenient for a broader audience. Understanding the differences between these charging options empowers EV owners to make informed decisions, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation future.
*source : power electronics news